
- #ANKLE SURGERY OPEN REDUCTION INTERNAL FIXATION SKIN#
- #ANKLE SURGERY OPEN REDUCTION INTERNAL FIXATION FULL#
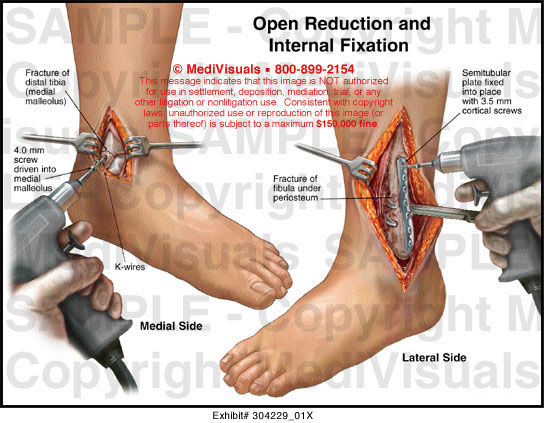
The process of actually joining the bones together is known as internal fixation, and it may entail the use of screws, rods, plates, wires, or nails. To get to the bones that need to be repaired, the surgeon might have to make multiple incisions. The bones have broken into multiple piecesĪn orthopaedic surgeon realigns the fractured bones to aid in the healing process during an open reduction procedure.
#ANKLE SURGERY OPEN REDUCTION INTERNAL FIXATION SKIN#
The broken bones have punctured the skin.The ankle bones are significantly misaligned.
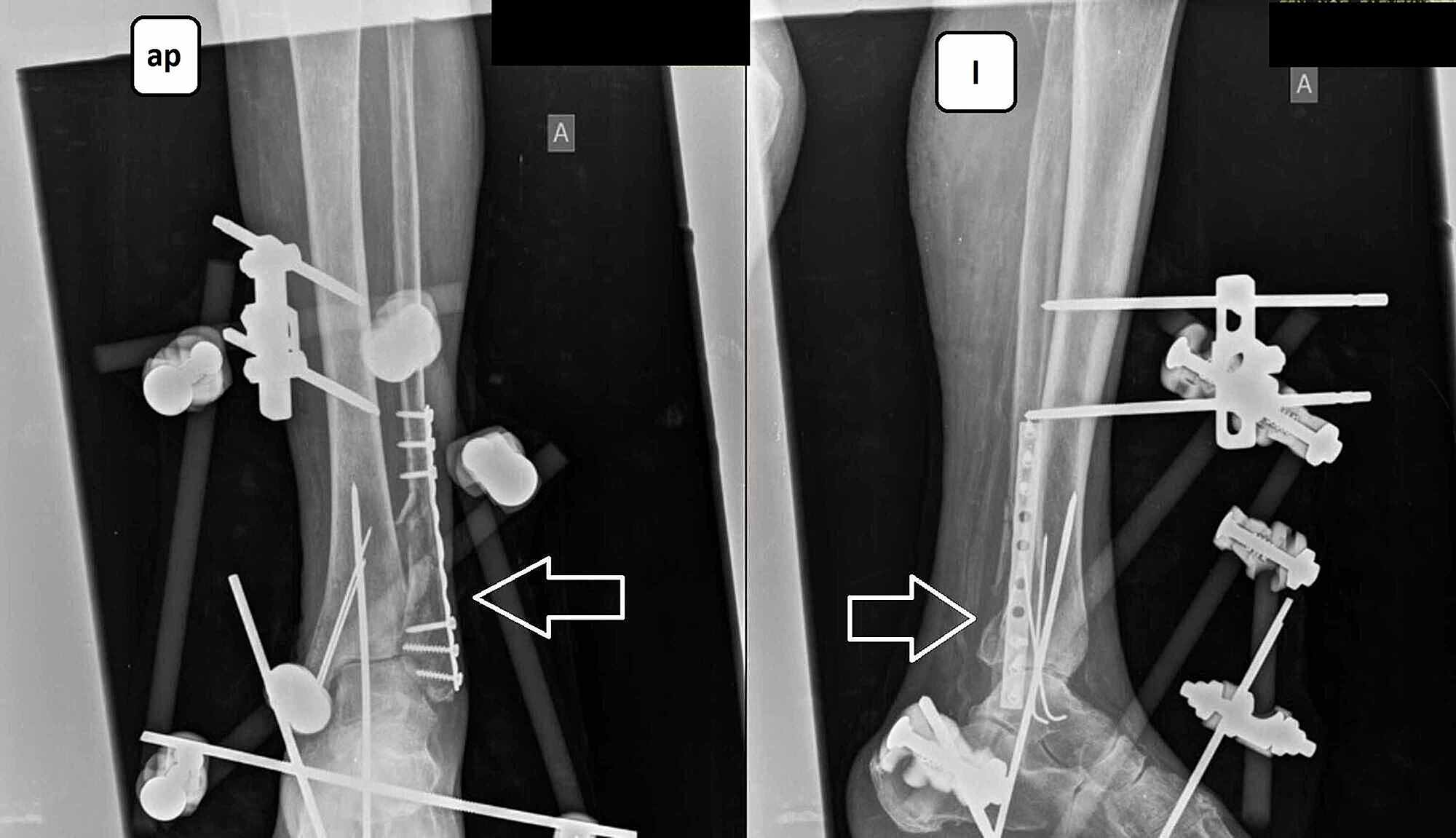
Ankle ORIF patients might be a suitable fit if: If the damage causes the ankle to become totally unstable, the fracture is deemed serious. An orthopaedic surgeon may attempt, under certain circumstances, to manually manipulate the broken bone through the skin before immobilizing the ankle completely in a plaster cast for a few weeks.
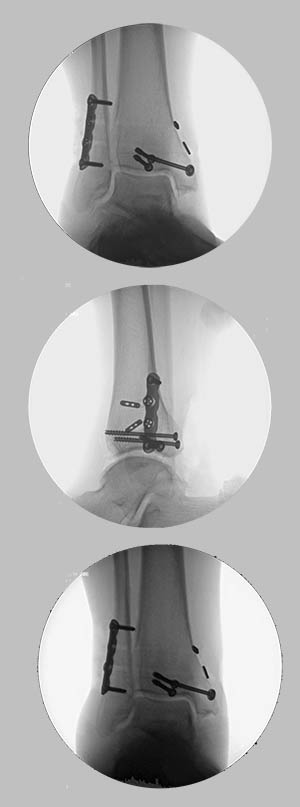
Health professionals are likely to recommend more conservative therapies, such as over-the-counter pain relievers, braces or casts, and physical therapy, for less serious fractures. Usually, ankle ORIF is not the first choice for treating fractured ankles. It is applied to one or more of the ankle joint’s three bones: Ankle fractures can occasionally cause ligament injury as well, which adds to the instability.Īnkle fractures can be stabilized and healed by an ankle ORIF (ankle fracture open reduction and internal fixation) procedure. A single fracture in one bone, which might not prevent a patient from walking, to several breaks in multiple bones, which drive the ankle out of position, can all indicate the severity of a fractured ankle. All rights reserved.In the U.S., one in eight hundred people experience an ankle fracture each year. With improved arthroscopic efficiency, the cost differential can be further reduced. In the acute treatment of ankle fractures, concurrent arthroscopic evaluation does not add a significant cost to the procedure and may result in improved short and long term benefits for the patient.
#ANKLE SURGERY OPEN REDUCTION INTERNAL FIXATION FULL#
Twelve of the 28 arthroscopic patients (42.86%) had grade 3 or full thickness chondral lesions, and 11/28 (39.28%) arthroscopic patients were found to have grade 1-2 cartilage changes. The cost difference between the ORIF only and with arthroscopy was not statistically significant (p = 0.1174). Total direct costs, including operating room time, for the same procedures were found to average $6,212.34 and $7,312.10 for the ORIF only and ORIF and scope procedures respectively. Total surgical costs averaged $6,537.62 and $6,886.46 for the ORIF only and ORIF and scope procedures respectively. There were 567 total ORIF and 28 ORIF and scope included for cost analysis purposes. Patient demographics, fracture characteristics, outcomes, and cost data were collected and analyzed. The primary purpose of this study was to determine the cost effectiveness of ankle arthroscopy performed at time of ORIF for ankle fracture.Īn IRB approved retrospective review of patients who sustained ankle fractures and underwent ORIF with and without concomitant arthroscopic surgery between 20 were investigated. Despite studies revealing intra-articular pathology in up to 79% of ankle fractures, only 1% of open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF) procedures undergo arthroscopic evaluation. Ankle fractures are a common orthopedic injury that frequently involves associated cartilage lesions, soft tissue damage, and a significant inflammatory burden.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
